機械学習に基づく
自然言語処理勉強会
第3回
@ナビプラス
中村晃一2014年12月4日
謝辞
この会の企画・会場設備の提供をして頂きました
㈱ ナビプラス様
にこの場をお借りして御礼申し上げます.
文書のクラスタリング問題
クラスタリング問題とは?
機械学習における クラスタリング (clustering) とは,データ $\mathbf{x}_1,\mathbf{x}_2,\ldots,\mathbf{x}_N$ をその距離や類似度に基いてグループに分けるという問題です.
前回やった分類問題では訓練データが与えられそれを学習しましたが,クラスタリング問題ではデータの特徴に基づき 教師なし (unsupervised) で分類を行うという点が異なります.
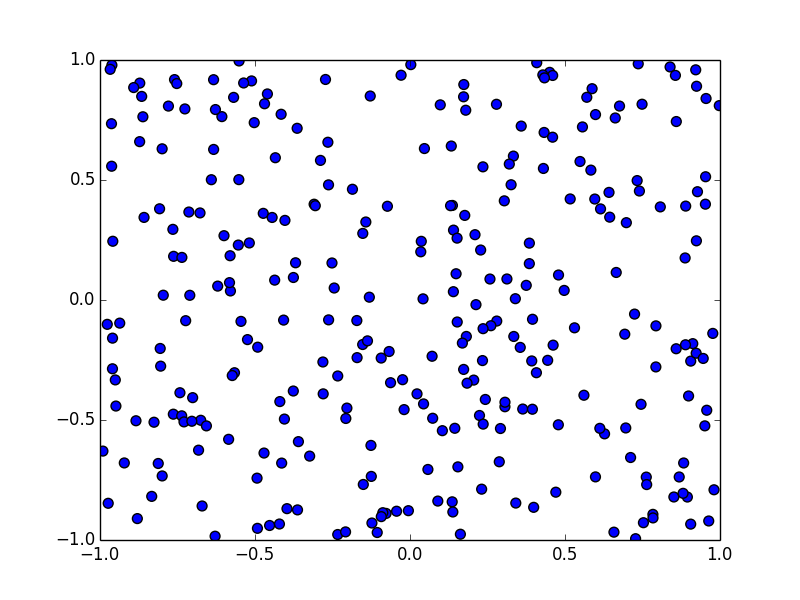
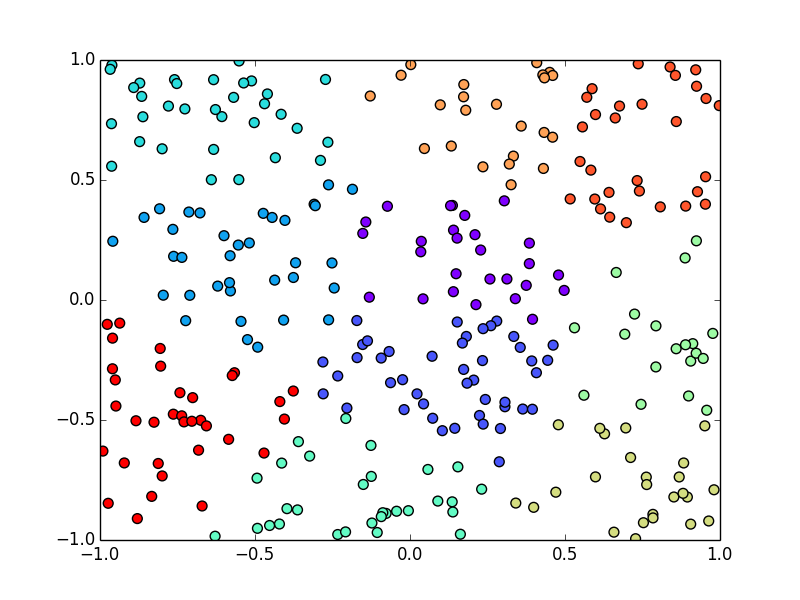
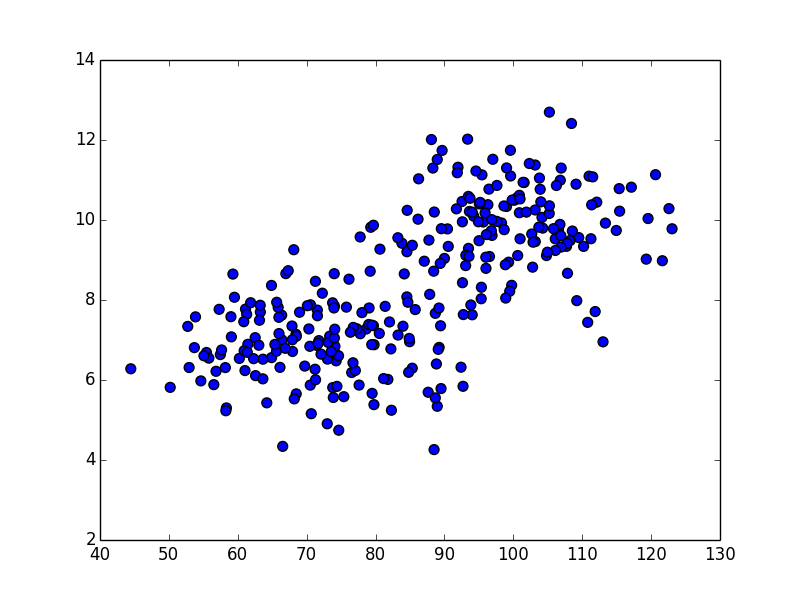
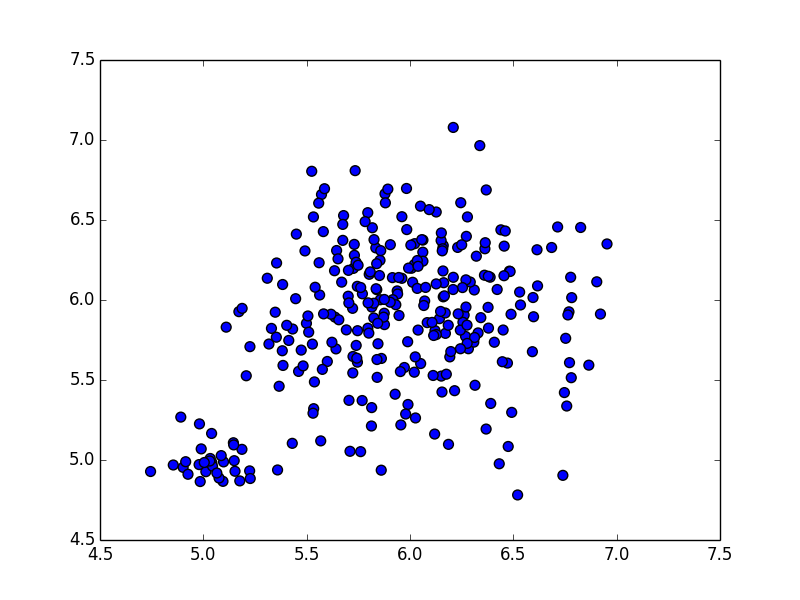
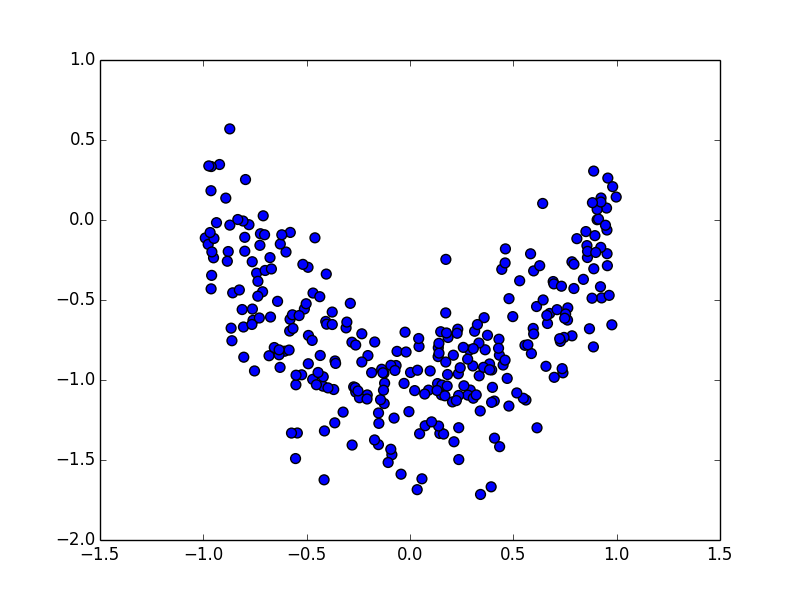
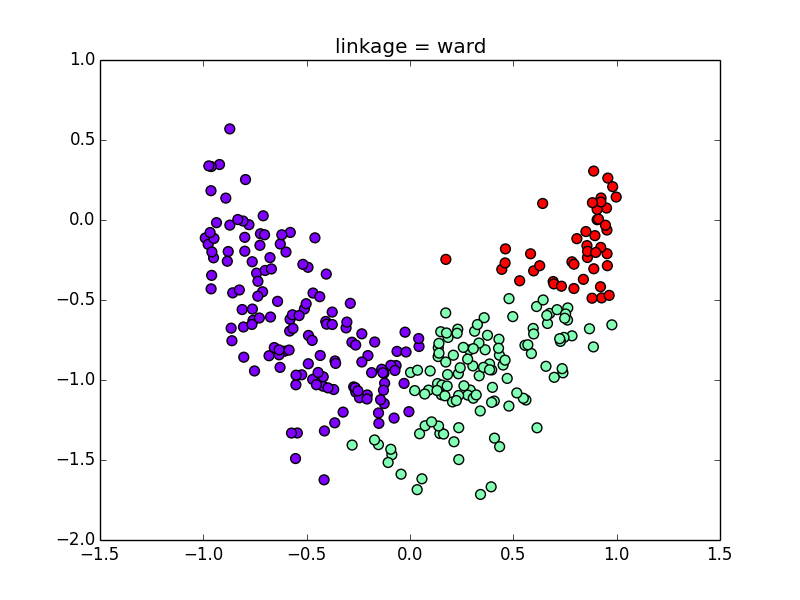
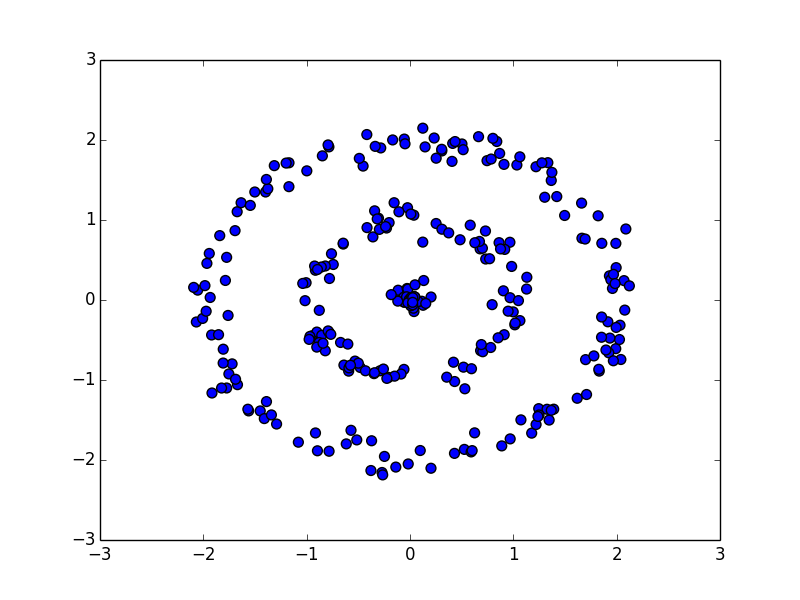
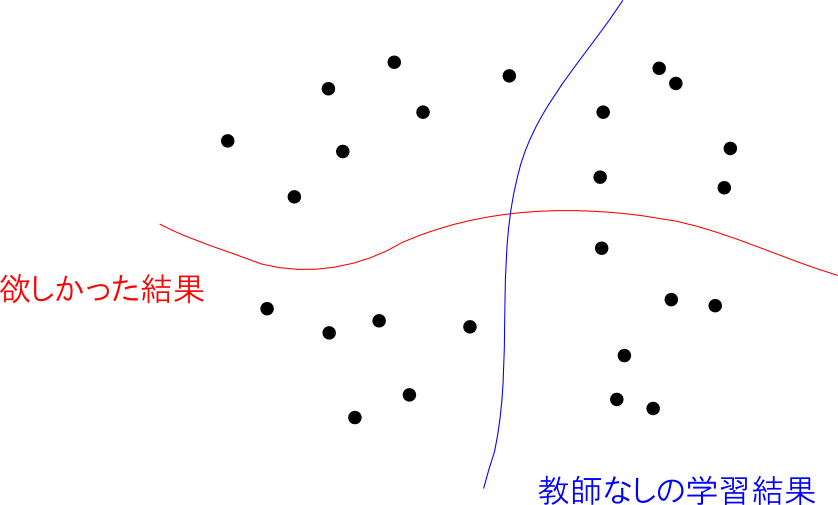
例えば,以下の二次元のデータをユークリッド距離に基いて10クラスに分けてみると
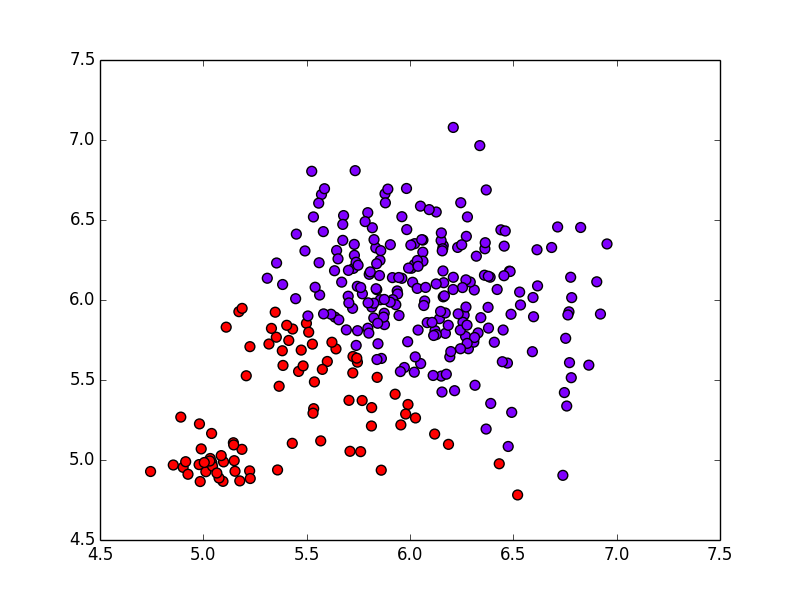
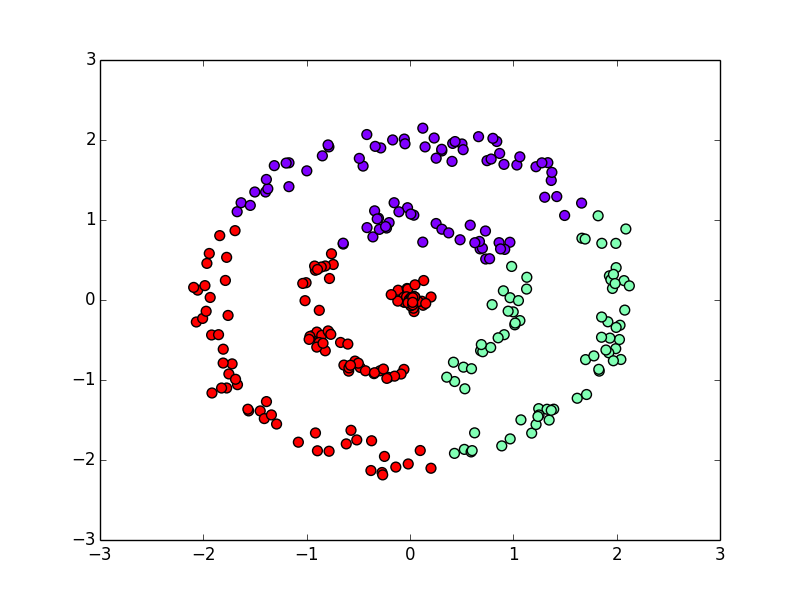
以下のようになります. 後述するK-means法を使っています.
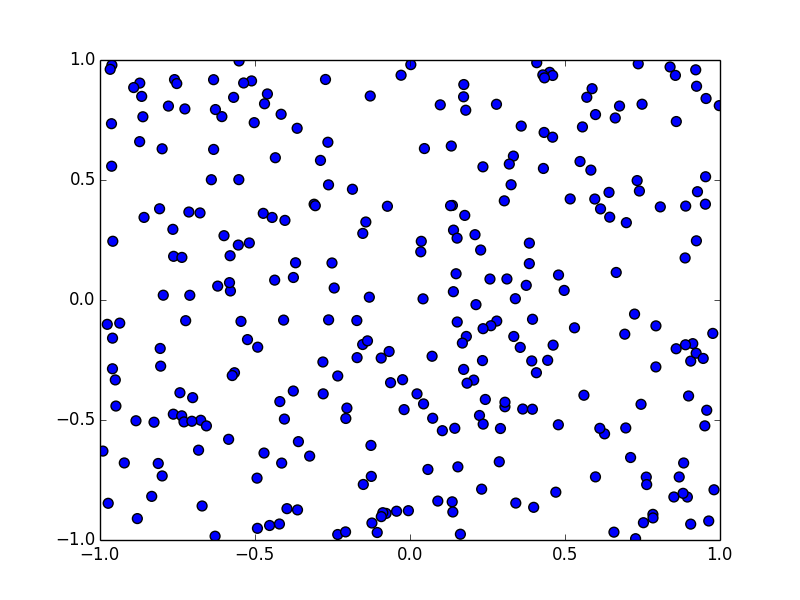
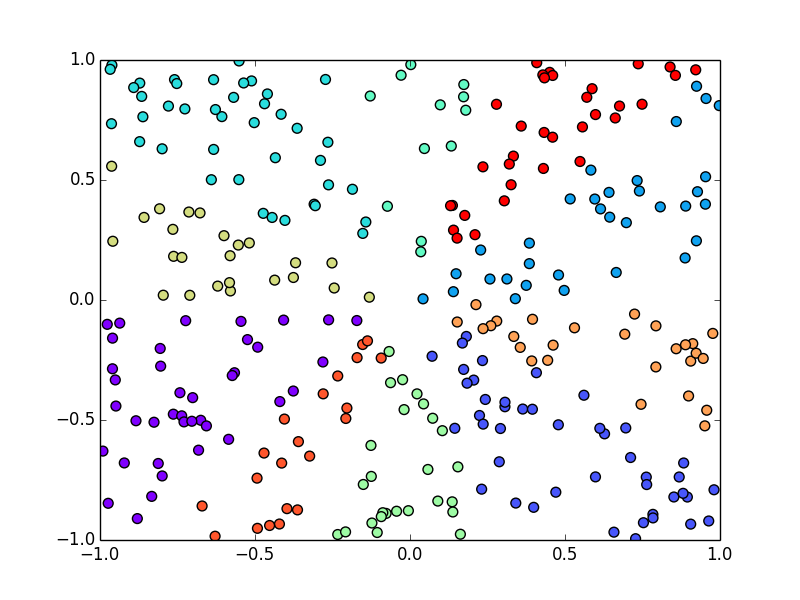
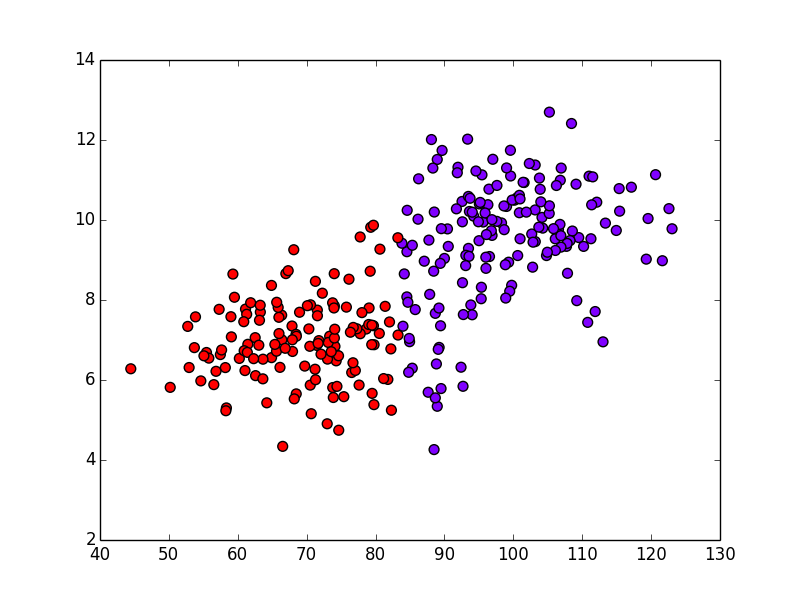
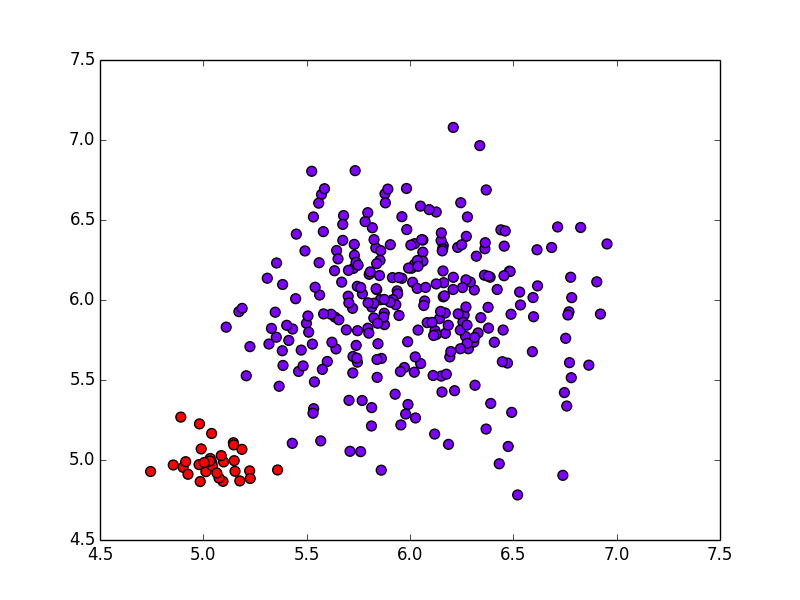
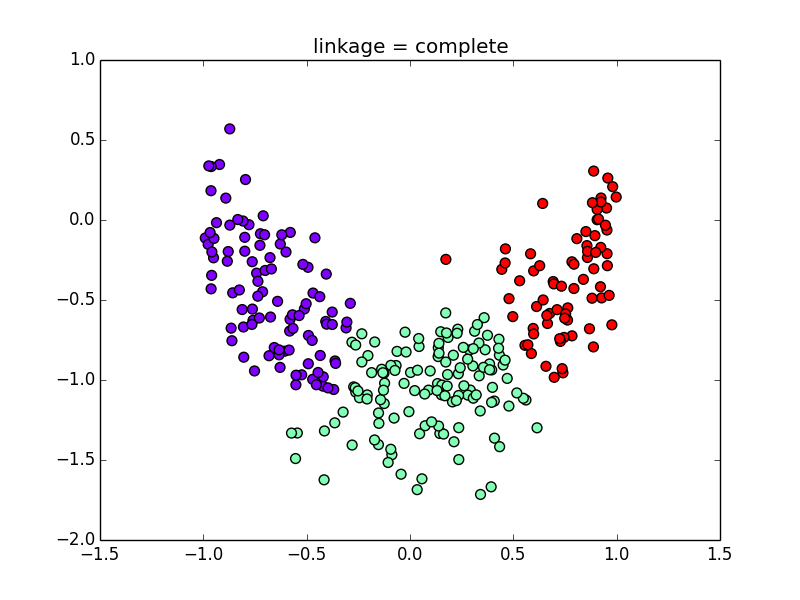
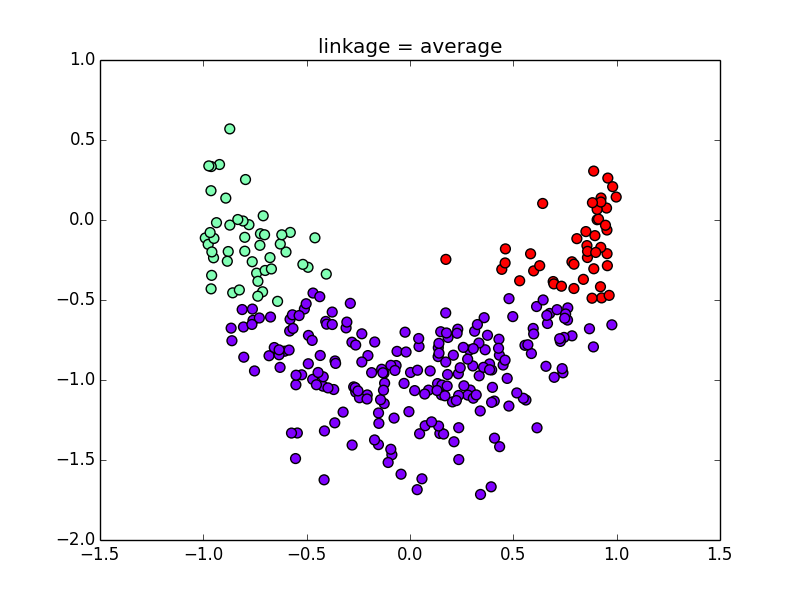
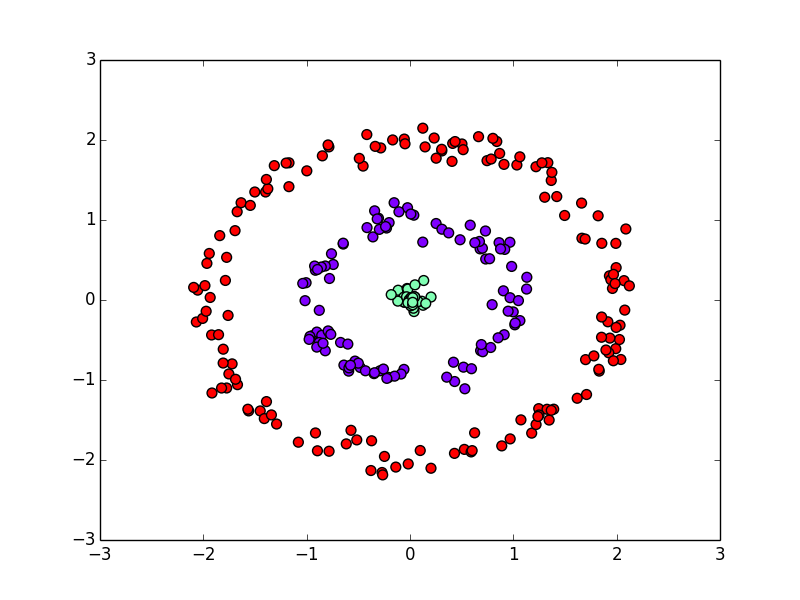
コサイン類似度でクラスタリングしてみると
以下のようになります. こちらでは群平均法というものを使っています.
分類とクラスタリングの比較
学習用データを用意するというのは非常に大変ですが,教師なし学習ではその手間が不要となります.
しかし, 教師なしだと求めていた結果とは全く異なる結果が得られてしまう可能性があります. 教師付きの分類では、問題に合わせて与える教師データや分類手法を設計する事が可能です.
クラスタリングが特に有用であるのは,運用フェーズよりも分析フェーズにおいてです.
ある大きな集団が,どのような集団から構成されているのか?といった事を分析する事が出来ます.
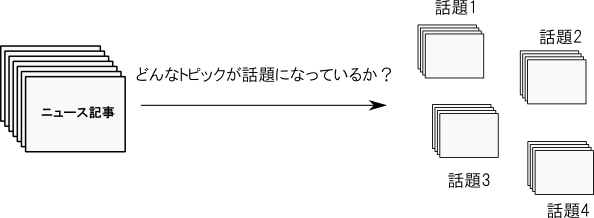
典型的な応用例は文書の集合からのトピックの抽出です. 例えばニュース記事をクラスタリングして,どのような話題が存在するのかを分析する事が出来ます.
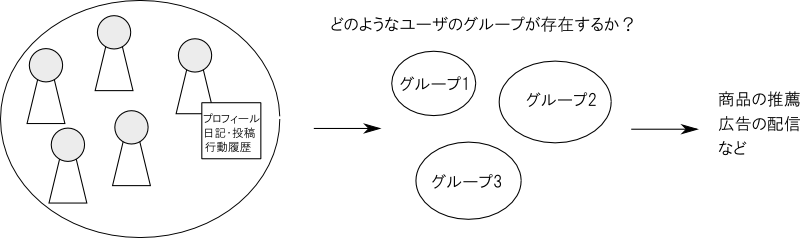
ユーザのプロフィール,投稿の内容,行動履歴などに分析を掛ければ,どのようなユーザーのグループが存在するかを調べる事が出来ます.
この結果を,広告の配信や商品の推薦などに役立たせる事が出来ます.
特徴ベクトルの設計が重要
クラスタリングではデータの分布の様子だけを手がかりに分類を行うので,教師付きの分類問題に比べ特徴ベクトルの設計,特に適切な変数選択を行う事が重要です.
また,使用する距離・類似度に応じて特徴ベクトルに適切な前処理を行う事も必要です.
例えば,特徴ベクトルの素性の中に「私は」「僕は」「です」「ます」「である」「だ」などの単語が含まれていたとします.
頻度ベクトル表現を使った場合には,これら非常によく出現する単語が距離や類似度に大きく寄与するので
- 文章の内容に基いてクラスタリングしたかった
としても
- 口調が似ている文章か否かが効いてしまった
という事が起こります.
また,絶対値が大きく異る複数の変数を使うと絶対値の大きい変数が支配的になってしまい,期待する結果が得られません.
例えば,以下の分布を見て下さい. 2つの集団があるのが見えます.
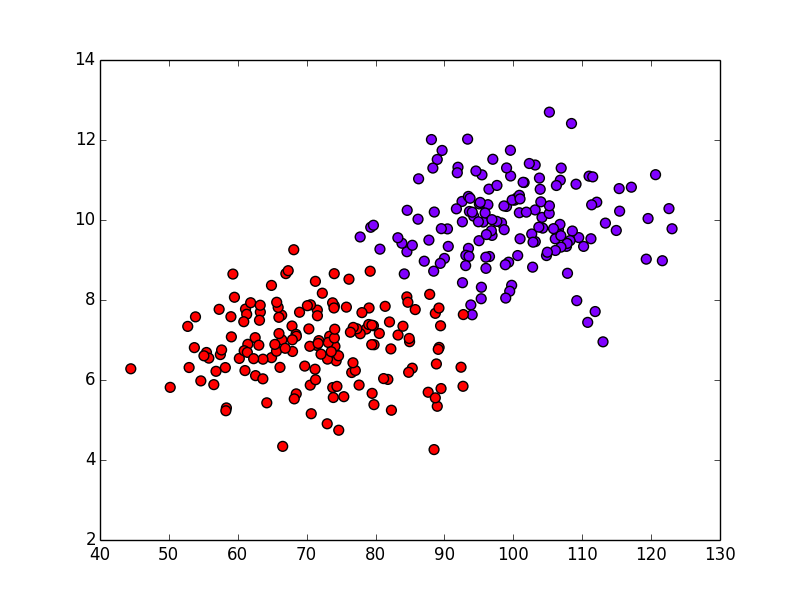
これに対して,ユークリッド距離に基づくK-means法というクラスタリング手法を適用すると以下の結果になってしまいます.
横軸の値の方が10倍ほど大きく,こちらがユークリッド距離の値を支配してしまう為です.
このような場合には,各変数 $X_i$ 毎に \[ X_i' = \frac{X_i - \overline{X}}{s[X]} \] という正規化を行う事が必要です. $\overline{X}$ は変数 $X$ の標本平均, $s[X]$ は変数 $X$ の標本標準偏差であり,これによって変数 $X'$ は平均 $0$, 標準偏差 $1$ に正規化されます.
先ほどの例に正規化を掛けたのが下の図です.
これに対してK-means法を適用すると以下のようになります. 期待通りの結果になりました.
まとめると,
- クラスタリングは教師なしで,集団を小集団に分解する手法である
- 特に分析フェーズにおいて有用である
- 特徴ベクトルの設計の良し悪しは教師あり学習の場合よりも大きい
となります. 以下,重要な手法を紹介します.
クラスタリングの手法
K-means法
K-means法 (K-means method)は非常に手軽で良く利用されるアルゴリズムです.
学習ベクトル $\mathbf{x}_1,\ldots,\mathbf{x}_N$ を $K$ 個のクラス $C_1,\ldots,C_K$ に分けた際に 歪み測度 (distortion measure) \[ \color{red}{ J = \sum_{k=1}^K \sum_{\mathbf{x} \in C_k}||\mathbf{x}-\boldsymbol{\mu}_k||^2 } \] が最小となるような,割り当て $C_1,\ldots,C_K$ を見つけます. $\boldsymbol{\mu}_k$ はクラス $C_k$ の重心で \[ \boldsymbol{\mu}_k = \frac{1}{|C_k|}\sum_{\mathbf{x} \in C_k}\mathbf{x} \] となります. $K$ はあらかじめ適当に決めておく必要があります.
K-means法ではデータ数 $N$,クラス数 $K$ に対して $\mathcal{O}(NK)$ の計算を数回繰り返します. 反復回数は一般に $N$ や $K$ よりも十分小さいので,ほぼ $\mathcal{O}(NK)$ の計算量だと思って良いです.
前頁の立式では,ユークリッド距離 \[ ||\mathbf{x}_i - \mathbf{x}_j|| \] が2つのデータ $\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j$ の距離として使われていましたが,これは任意の距離 $d(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j)$ に一般化して \[ J = \sum_{k=1}^K \sum_{\mathbf{x} \in C_k}\{d(\mathbf{x},\boldsymbol{\mu}_k)\}^2 \] を考える事も可能です.この場合の計算時間も $d$ の計算が定数時間ならば $\mathcal{O}(NK)$ です.
K-means法では(多くの他のアルゴリズムのそうですが)歪み測度 \[ J = \sum_{k=1}^K \sum_{\mathbf{x} \in C_k}\{d(\mathbf{x},\boldsymbol{\mu}_k)\}^2 \] の最小化が保証されているわけではありません. 大抵は局所最適解に陥ってしまいます.
実行する度にその結果が変化しますので,複数回実行し結果を総合的に判断する事が必要です.
K-means法では EMアルゴリズム (expectation maximization) というものが用いられます. 詳しくは パターン認識・機械学習勉強会第18回 を参照して下さい.
例
20 newsgroups dataset の約1万1000文書にK-means法を適用してみましょう. $K=10$ としてどのような話題が話されているか調べてみます.
まず特に工夫せずに,unigramのTf-Idfを特徴量として使ってみましょう.コードは以下です.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from numpy import *
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
df = fetch_20newsgroups()
# Tfidf表現に変換し,K-meansでクラスタリング
K = 10
vec = TfidfVectorizer()
data = vec.fit_transform(df.data)
cls = KMeans(n_clusters=K)
labels = cls.fit_predict(data)
# 各クラスの重心において,寄与度の高い単語上位10個を表示
for k in range(K):
print "class %d:" % k,
center = cls.cluster_centers_[k]
words = argsort(center)[-10:]
print " ".join(reversed([vec.get_feature_names()[w] for w in words]))
結果は以下のようになります. 各クラスの重心において,Tf-Idfが大きい上位10単語を並べています. theやandなど意味のない単語ばかりになってしまいました.
class 0: scsi drive the ide to controller and drives disk hard
class 1: the to of and that is in you it not
class 2: washington edu the carson of seattle to in shelley eliot
class 3: the edu to of for in and com from is
class 4: keith caltech livesey sgi the solntze wpd morality schneider that
class 5: cmu andrew the carnegie mellon edu pittsburgh to pa and
class 6: the to of and in is that it you for
class 7: geb banks gordon pitt the cs is dsl n3jxp cadre
class 8: the he to in and of team that was is
class 9: cleveland cwru edu freenet the reserve ins western to po
そこで,単純な改善としてdocument frequencyが10%以上のものは素性として使わない事にしてみます.
コードは prog3-6.pyです. 結果は以下のようになり,どのような話題が話されているのかよく分かるようになりました. このように特徴ベクトルを上手く選ぶ事が重要です. 実行時間は63.9秒でした.
class 0: israel israeli jews arab jake arabs lebanese israelis adam policy
class 1: drive scsi card mac apple ide monitor video bus controller
class 2: god jesus christians bible christian christ faith church sandvik christianity
class 3: nasa space gov keith henry caltech msg alaska livesey jpl
class 4: key clipper encryption chip escrow keys government crypto algorithm nsa
class 5: turkish armenian armenians armenia ax turks argic turkey serdar genocide
class 6: uk ac co ___ mathew mantis cam dcs ed bnr
class 7: car year cc game team hp david gun him netcom
class 8: geb banks gordon pitt dsl n3jxp chastity cadre shameful skepticism
class 9: windows file window dos files program graphics mouse ms version
混合ガウスモデル
各クラス $k$ のデータが,それぞれ正規分布 $\mathcal{N}(\boldsymbol{\mu}_k, \Sigma_k)$ に従うと仮定すれば観測データは 混合ガウス分布 (mixture Gaussian distribution) \[ p(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{k=1}^K \pi_k \mathcal{N}(\boldsymbol{\mu}_k, \Sigma_k) \] に従います. $\pi_k$ はクラス $k$ のデータが出現する確率です.
最尤法によって $\boldsymbol{\mu}_k,\Sigma_k,\pi_k$ を求めれば,各データ $\mathcal{x}_i$ がクラス $k$ に所属する確率を計算する事が出来ます. これを使ってクラスタリングを行う事が出来ます.
実際,K-means法は混合ガウスモデルのある種の極限を取ったものです. (詳しくはPRML本の第9章)
混合ガウスモデルでは単なる集合としてのクラスタではなく確率分布として各クラスタを求める事が出来ますのでより詳しい分析が可能になります.
K-meansと混合ガウス分布の差が顕著に現れる例は,分布毎に分散が異なる場合です. 例えば,以下の例に適用してみます.
K-means法では以下のようになります. 上手くクラスタリングが出来ていません.
混合ガウスモデルの場合は以下のようになります. 上手く2つの集団を取り出すことが出来ています.
問題点は,各データ $\mathbf{x}_i\quad (i=1,\ldots,N)$ が各クラス $k\quad (k=1,\ldots,K)$ に所属する確率をそれぞれ計算しなければならないので, 単純な実装では $N\times K$ の記憶領域が必要になるという事です.
また,パラメータ数が増加しますので過学習に注意が必要です. 特に分散共分散行列 $\Sigma$ は特徴量の数の二乗のパラメータを持つので注意が必要です. 従って $\Sigma_k$ が対角の場合のみを考えるなどの工夫が行われます.
20 Newsgroups datasetに使ってみましょう. コードは prog3-8.pyです. ここでは$\Sigma_k=\sigma_k^2 I$と書ける場合のみを考えています. さらに,document frequencyが50回以上かつ0.5%未満の単語のみを特徴量として使っています. それでも実行時間は5分ほどかかります.
class 0: alaska aurora nsmca dseg ti gene crazy fly taxes wright
variance: 0.00128869046085
class 1: sandvik armenians mcgill serdar turkey argic arabs uci cramer adam
variance: 0.00142081458615
class 2: simms duke wpi meg isa quadra diamond gif ati cache
variance: 0.00142639920386
class 3: henry spencer zoo lunar shuttle film dseg orbital ti fuel
variance: 0.00130076108747
class 4: uchicago ncr nec udel stratus portal umich iastate bikes honda
variance: 0.00143137269973
class 5: informatik encrypted wiretap gtoal eff walker ncsu cryptography colostate eos
variance: 0.00142311387924
class 6: upenn cornell braves sas espn leafs cunixb pitching rangers uwo
variance: 0.00142664772482
class 7: geb msg cadre skepticism shameful n3jxp chastity dsl intellect sensitivity
variance: 0.00133972460979
class 8: isc nz atheism livesey rit wpd schneider solntze mathew allan
variance: 0.0014135641046
class 9: usc widget x11r5 xterm font expo xt xpert xlib fonts
variance: 0.00142285201768
混合ガウスモデルも EM法 を利用します. 詳しくはやはり パターン認識・機械学習勉強会第18回 を参照して下さい.
凝集型クラスタリング
ここまで紹介したK-means法,混合ガウスモデルは「最適な分割を見つける」という考え方に基づいており 分割型クラスタリング (partitional clustering) と呼ばれます.
これと異なる考え方に 凝集型クラスタリング (agglomerative clustering) というものもあります.
凝集型クラスタリングでは,まず全てのデータをそれ1つだけでクラスタとみなします.
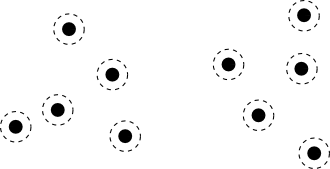
続いて,クラスタ $C_i$ と $C_j$ の何らかの距離 $d(C_i, C_j)$ が最も近いクラスタ同士を併合する事によってクラスタの数を減らします.
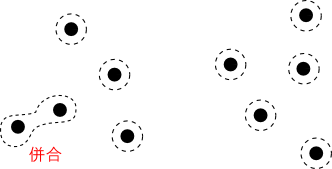
これをクラスタ数が所定の数 $K$ になるまで,もしくは何らかの停止条件にたどり着くまで繰り返す事によってクラスタリングを行う事が出来ます.
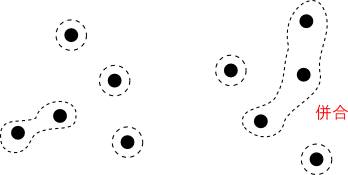
クラスタ $C_i$ と $C_j$ の距離 $d(C_i,C_j)$ はデータの距離 $d(\mathbf{x}_p,\mathbf{x}_q)$ に基いて計算するのが一般的です.
- 最長距離法 (complete linkage) \[ d(C_i, C_j) = \mathop{\rm max}\limits_{\mathbf{x}_p\in C_i,\mathbf{x}_q\in C_j} d(\mathbf{x}_p,\mathbf{x}_q) \]
- 最短距離法 (nearest neighbor linkage) \[ d(C_i, C_j) = \mathop{\rm min}\limits_{\mathbf{x}_p\in C_i,\mathbf{x}_q\in C_j} d(\mathbf{x}_p,\mathbf{x}_q) \]
- 群平均法 (group average linkage) \[ d(C_i, C_j) = \frac{1}{|C_i||C_j|}\sum_{\mathbf{x}_p\in C_i,\mathbf{x}_q\in C_j} d(\mathbf{x}_p,\mathbf{x}_q) \]
- Ward法 \[ d(C_i, C_j) = J(C_i\cup C_j) - J(C_i) - J(C_j) \]
Ward法における $J$ はK-meansで登場した歪み測度です. これは $C_i,C_j$ を併合する事によって増加する歪み測度の大きさを表しています.
出来るだけクラスタを歪ませない様に併合を行っていくというアルゴリズムであり,K-means法に近い効果があります.
例
対称的でない分布を使うと指標による差がよく解ります. Ward法,最長距離法,群平均法について見てみましょう.
Ward法
最長距離法(各クラスタが出来るだけコンパクトになる)
群平均法(計算しやすいが,偏りが出やすい)
20 Newsgroups datasetでのコード例は prog3-12.pyです. 最長距離法を使っています. かなり計算時間が掛かるので,ランダムに2000文書だけ選んでクラスタリングを行っています. 実行時間は約100秒です.
class 0: netcom uiuc jesus alaska fbi morality batf turkish craig government
class 1: windows uk card ibm ohio cc ac key software apple
class 2: 00 sale kevinh pts 12 ascom hasler 11 15 20
class 3: god gun bible christians hell christian life armenian kratz faith
class 4: nec ground berkeley behanna wire wiring engine centaur neutral david
class 5: files db windows image cc cview vma paula vga dseg
class 6: nus sg nuscc sergei singapore human national scum nusunix1 godless
class 7: encryption clipper chip nmsu government privacy intercon water amanda zisfein
class 8: israel israeli usc aids ed suite sun palestinian crime jews
class 9: she car space cmu insurance her health andrew isc oil
DBSCAN法
DBSCAN (density based spatial clustering of applications with noise) はグラフ理論的な考え方に基づくアルゴリズムです. 面白い方法なので紹介しておきます.
データ $\mathbf{x}$ からデータ $\mathbf{y}$ への到達可能性を以下が両方成り立つ事と定義します.
- $\mathbf{x}$ と $\mathbf{y}$ の距離 $(\varepsilon)$ がしきい値より近い
- $\mathbf{x}$ の周囲に十分な数のデータ $(minPts)$ が存在する
データの密度の高い箇所を起点とし,この到達可能性関係を辿って到達出来るデータを1つのクラスタとします.
DBSCANは任意の形状のクラスタを抽出する事が可能です. 一方,K-meansなどこれまでに紹介した方法は対称性のある分布を前提としています.
人工的に作った以下の分布で試してみましょう.
K-meansだと以下のようになります.
以下はDBSCANの結果です.
DBSCANはデータの密度に基いているので,スパースな(スカスカな)データセットのクラスタリングには向きません.
自然言語のような複雑な対象は,クラスタの分布がどのような形状をしているかが明らかではない為,面白い結果が出てくる可能性はあります.
計算量が高い(文書数 $N$ に対して $\mathcal{O}(N^2)$ 程度)ので20 Newsgroups dataset からランダムに5000文書を選んでDBSCANを実行してみました(prog3-14.py). 到達可能性判定に使うパラメータは $\varepsilon = 0.9, minPts = 5$ としました. 結果以下の72クラスタが学習されました.
class 0: intercon amanda walker herndon tcp chaos restrictions feds gtoal worried
class 1: randy msc hooked pas sec loaded wailing seagate grinding nu
class 2: uga mcovingt covington athens aisun3 706 542 n4tmi 0358 7415
class 3: buffalo ubvmsb def standings 28th architecture gods weiss ye luke
class 4: dseg mccall ti mksol 575 mary dryden nuclear balls prb
class 5: ink deskjet mod nd rain pictures wet taylor brunel isis
class 6: serdar 494 cute 617 4th loser abortion wasted argic nationality
class 7: kratz glocks glock trigger uic uicvm u28037 newshost 93104 sail
class 8: philips netherlands laboratories winter licensed interfaces buttons wires phillips pins
class 9: oracle crashing keeps geometry parity crash simms parse manually consistently
class 10: journalism ep riddle grand mlb marlins marks tigers gonna trips
class 11: ini updating bailey exe odin portal script automatic adrian edit
class 12: sandvik kent newton ksand alink cookamunga tourist arromdee bureau jhu
class 13: stream blocks transmission loral session protocols plaintext mutilated spatial hostile
class 14: cramer optilink clayton gay homosexual promiscuous sexual male partners pyramid
class 15: stratus sw cdt tavares vos investors packet 508 libertarian carl
class 16: jagr francis stat uvic gibson ubc minus gballent hudson evident
class 17: nwu acns casbah crimes charged br northwestern bashing thf2 beating
class 18: nada kth tte d88 jwa deluxe hacker stockholm royal sweden
class 19: gl widget xt xlib mix widgets mwm xpert expo csc
class 20: claremont ebrandt eli jarthur mitre qualcomm brandt denning servo feared
class 21: eos ncsu mitch wrench brief hearing waters caps buffalo fox
class 22: behanna nec syl cb360t fxwg glide jubilee corn zx 1975
class 23: planes karabakh homeland henrik azeris kurds su searched content azerbaijan
class 24: lehigh ns1 danny gt sports rx 1993apr17 ranges _______________________________________________________________________________ tragedy
class 25: 610 centris scrolling push configured horizontal vertical spare observed disappear
class 26: ch981 alicea hela shades lodge oriental sandvik kent invading newton
class 27: livesey solntze wpd species gap schneider assign immoral fido intelligent
class 28: ysu yfn ak296 daker einstein youngstown albert elizabeth solved 650
class 29: differ oft lite multitasking ing rmohns arise clarku netware til
class 30: qualcomm rdippold qualcom dippold asbestos spy congressional espionage denning spending
class 31: ksu matt boot connects kansas kent ctrl mhz peak yield
class 32: greeks treaty french unsw turk enforce germans allied rejected ottoman
class 33: dresden tu inf beck shading irs andre shade xputimage mahan
class 34: dyer spdcc ima rayssd m2c ursa linus aka seizures consulting
class 35: risc instruction nctu tw mq reduced linux pentium mpce addressing
class 36: alaska aurora nsmca mining acad3 jacked fairbanks adams prb eco
class 37: sdsu xt umn todd fixing ian 612 widget theodore larc
class 38: dma mastering valve uwo wayne transfers 200mb adapter xga increasing
class 39: rpi ecs polytechnic sphere kim danny capability ordered gifs stadium
class 40: beckman arthur instruments rubin corporations japanese entity compromised mcimail 453
class 41: duke acpub durham sutherland dammit 71 bellcore liability nf parking
class 42: gwu louray seas panayiotakis bmp mickey pe wpi gd ace
class 43: rebound chuck acad diet gaining substantiate oral constitute exceeds researchers
class 44: rmohns hex clarku licensed ahh encoded mu relation mistaken registered
class 45: convex rocks tobias erik pound richardson bridges abort lbs ours
class 46: espn wustl cec1 cubs rained astros thumbs leafs playoffs stanley
class 47: witnesses gm thf2 wright screwed desire kimbark stein2 boomer tzs
class 48: xerox marty 415 slick palo cheapest 315 pdt oral mc
class 49: b30 beam ingr radar bellcore ski huntsville intergraph 205 1993apr2
class 50: cursor diamond nih fsu menus wondered distortion delivered indication chem
class 51: larc langley riots tests dig occasional polish democrat teaching pushed
class 52: ico beauchaine bobbe vice tek gregg jaeger islamic livesey blew
class 53: msg chinese rogers flavor bellcore superstition sensitivity jchen restaurant meat
class 54: nyeda eau uwec cnsvax nye philosopher patently clinic wi wishes
class 55: ax pl 145 wm sl gk 3l 9v m3 bj
class 56: cdac ole brandeis prelude devil pins speaker 87 panel vw
class 57: uio ifi norway crimes masses viking handheld informatics defend iastate
class 58: hitter torre pinch alicea bases bench inning jordan luis outs
class 59: seth acpub duke oak grayscale archie vesa meg arkansas whats
class 60: howland curt arc dogs ace 82 eff fsu bikers waves
class 61: cruel constitution punishment founding hanging painful fathers schneider firing meanings
class 62: weaver randy harris sps betz gozer inches agent reporter gerry
class 63: umanitoba ccu frame beleive der paint uh floppies clara manitoba
class 64: albany albnyvms eve attending aka publicity saturday tonight fees csc
class 65: polygon convex polygons edges postscript usc bull simon bound clipping
class 66: oakland atterlep vela disorganized ximenez cardinal messiah sexual relations approached
class 67: hydro jody levine rd jlevine kv 275 helmet highway helmets
class 68: parr ucalgary echoing gourd hollow conjoined chord span threads struck
class 69: harris ssd ft fl timothy languages everytime satanic miracle dcs
class 70: wpi jonathan polytechnic boxes tigers cant rash albeit overly calvin
class 71: mahan tgv lazarus gc waking washer drawing offense enterpoop xpert
第3回はここで終わります
次回は「系列ラベリング問題」を紹介します.